Understanding Grapevine Communication in the Workplace
“The grapevine is a natural part of a company’s total communication system.”
— Keith Davis
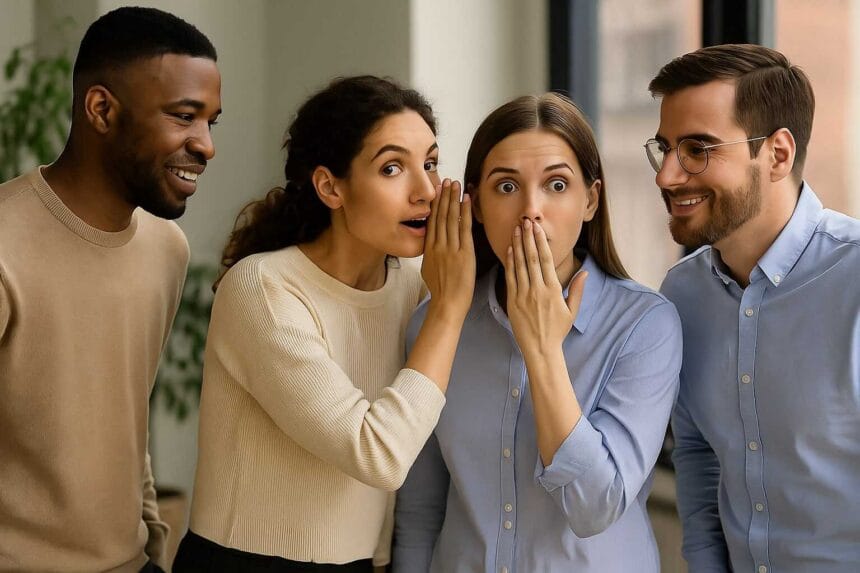
Grapevine communication is the informal network through which information spreads within an organization. Unlike formal communication channels, the grapevine relies on casual conversations, gossip, and personal interactions among employees.
This unofficial communication system is rapid and can reach a broad audience faster than formal channels like emails or meetings. However, its lack of formal structure and documentation can lead to misinformation and impact employee morale and company culture.
Understanding grapevine communication is crucial for managers to leverage its benefits and mitigate its potential drawbacks. This blog post will explore the definition, spread, types, advantages, disadvantages, and management strategies for grapevine communication.
What is Grapevine Communication?
Grapevine communication refers to the informal, unofficial transmission of information within an organization. It occurs outside the established communication channels, typically through casual conversations and personal networks.
The term “grapevine” reflects the way information spreads—unstructured and in all directions, similar to the sprawling growth of grapevines. This informal network can carry both factual information and rumors or opinions, influencing employee perceptions and behaviors.
While not controlled by management, the grapevine plays a significant role in shaping workplace dynamics. When managed effectively, it can foster healthy team relationships. However, if ignored, it can breed confusion and distrust.
Quick Overview of Grapevine Communication
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Grapevine Meaning | The informal and unofficial way information spreads within an organization. |
| Origin | The rapid and multi-directional growth pattern of grapevines. |
| Phrase Origin | American Civil War soldiers likened telegraph wires to grapevines. |
| Year of Origin | Approximately the 1860s. |
| Types | Single Strand, Gossip Chain, Probability Chain, Cluster Chain. |
| Advantages | Speed, relationship building, feedback surfacing, morale boost. |
| Disadvantages | Rumor spreading, inaccuracy, trust erosion, productivity impact. |
| Tips to Manage | Clear communication, early rumor addressing, open channels, trust building. |
Examples of Grapevine Communication
Real-world examples illustrate how grapevine communication functions within a workplace, influencing employee experiences and perceptions.
Positive Example: News About a Promotion
- Scenario: Employees hear through informal channels that their team lead is likely to be promoted.
- Spread: The news circulates during breaks and casual conversations among team members.
- Result: Excitement and increased motivation as employees anticipate growth opportunities.
- Impact: Boosted morale and proactive engagement before the official announcement.
Negative Example: Layoff Rumors
- Scenario: A random comment sparks a rumor about impending layoffs.
- Spread: The rumor spreads rapidly across departments, causing worry and speculation.
- Result: Increased stress, decreased productivity, and some employees seeking new jobs.
- Impact: Fear and distrust due to the lack of official updates.
Types of Grapevine Communication
Grapevine communication manifests in various patterns, each characterized by the flow of information and the individuals involved.
1. Single Strand Chain
In this type, information passes linearly from one person to another:
> A → B → C → D
This method is slow and susceptible to distortion as the message passes through multiple individuals.
2. Gossip Chain
One person disseminates information to many others simultaneously:
> A → Multiple Recipients
This is common when the information is personal, dramatic, or exciting, but it often includes opinions rather than facts.
3. Probability Chain
Information spreads randomly, with individuals sharing it with a few others who may or may not pass it on. This is used when information is unclear or not urgent.
4. Cluster Chain
This is the most common type, where one person shares information with a few trusted individuals, who then share it with their own circles. This method is fast, personal, and difficult to trace.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Grapevine Communication
Grapevine communication has both benefits and drawbacks, making it essential to understand its impact on the workplace.
Advantages of Grapevine Communication
- Rapid Information Spread: Faster than formal channels, particularly in urgent situations.
- Team Bonding: Encourages connection and comfort among employees.
- Honest Feedback: Provides insights into real concerns and opinions.
- Morale Boost: Positive messages can improve mood and motivation.
- Early Warning System: Helps managers identify potential issues early on.
Disadvantages of Grapevine Communication
- Rumor Spreading: False information can cause panic and confusion.
- Trust Erosion: Misunderstandings and gossip can damage relationships.
- Reduced Productivity: Distractions from excessive talk and speculation.
- Lack of Accountability: Difficult to trace or correct false messages.
- Confusion: Mixed versions of information can leave employees uncertain.
Managing Grapevine Communication
While you can’t eliminate grapevine communication, effective management can turn it into a valuable tool.
Tips for Managing Grapevine Communication
- Keep Employees Informed: Provide regular updates through official channels to reduce reliance on gossip.
- Address Rumors Early: Clarify false information promptly to prevent its spread.
- Create Open Culture: Encourage questions and transparency to foster trust.
- Be Visible and Approachable: Managers should stay connected with their teams.
- Train Team Leaders: Equip supervisors to identify and address unhealthy gossip.
- Use Feedback Channels: Implement anonymous surveys and suggestion boxes.
- Lead by Example: Avoid engaging in gossip to set a positive tone.
FAQs About Grapevine Communication
What is grapevine communication in the workplace?
Grapevine communication is the informal exchange of information among employees, typically through word of mouth or group messages, rather than formal channels.
What are the characteristics of grapevine communication?
- Informal and unstructured
- Rapid spread across teams
- Travels through personal networks
- Includes facts, guesses, or opinions
- Driven by emotion or curiosity
- Not officially recorded
Where does grapevine communication exist in the organization?
Grapevine communication exists at all levels of an organization, between coworkers, across teams, and between junior and senior staff.
What are the types of rumors in grapevine communication?
- Wish-fulfillment rumors
- Fear-based rumors
- Wedge-driver rumors
- Home-stretcher rumors
How does technology shape modern grapevine communication?
Messaging apps and social media have accelerated the spread of grapevine communication, making it harder to control.
What are the factors affecting grapevine communication?
- Poor formal communication
- Strong informal social groups
- Uncertainty or lack of transparency
- Personal agendas
- Organizational culture
What’s the difference between grapevine and formal communication?
Grapevine communication is informal and fast, while formal communication is structured and follows a defined process.
Grapevine Communication vs. Formal Communication
| Feature | Grapevine Communication | Formal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Informal and unofficial | Official and structured |
| Speed | Spreads quickly | Follows a slower, defined process |
| Source | Unknown or anonymous | Clear and identified |
| Content | Opinions, rumors, or guesses | Factual and verified |
| Method | Conversations, chats, social talk | Emails, meetings, notices |
| Accountability | No accountability | Sender is responsible |
| Control | Hard to control | Easy to manage and trace |